
Metformin is a commonly prescribed medication for controlling blood sugar levels in patients with diabetes. However, individuals with end stage liver disease need to be particularly cautious when using this drug.
As liver function declines, the body’s ability to process medications, including metformin, is impaired. This can lead to a build-up of the drug in the system, increasing the risk of adverse effects.
If you have end stage liver disease and are prescribed metformin, it is important to work closely with your healthcare provider to monitor your condition and adjust your medication as needed to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Understanding Metformin and Liver Disease
Metformin is a commonly prescribed medication for the management of type 2 diabetes. It works by lowering blood sugar levels and improving insulin sensitivity in the body. However, there have been concerns about the potential impact of metformin on liver health, especially in patients with pre-existing liver conditions.
The liver plays a crucial role in metabolizing drugs, including metformin. While metformin is generally considered safe for the liver, some studies suggest that it may lead to rare cases of liver damage or liver failure, particularly in individuals with liver disease or other risk factors.
It is important for patients taking metformin to be aware of the potential risks and benefits of the medication, especially if they have a history of liver disease. Regular monitoring of liver function tests may be recommended for those at higher risk of liver complications.
| Key Points: |
|---|
| Metformin is commonly prescribed for type 2 diabetes management. |
| While generally safe for the liver, metformin can pose risks for individuals with liver disease. |
| Patients should be aware of the potential impact of metformin on liver health and discuss any concerns with their healthcare provider. |
Overall, understanding the relationship between metformin and liver disease is essential for healthcare providers and patients to make informed decisions about treatment options and potential risks.
The Link Between Metformin and Liver Disease
Metformin is a commonly prescribed medication for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. However, there has been some concern about its potential impact on liver health, particularly in patients with liver disease.
Understanding the Relationship
Metformin is primarily excreted by the liver and can accumulate in patients with liver disease, leading to potential complications. This accumulation can increase the risk of lactic acidosis, a serious condition that can be life-threatening.
Monitoring and Safety
Patients with liver disease who are prescribed metformin should be closely monitored by healthcare providers to ensure the medication is being metabolized appropriately and to watch for signs of lactic acidosis. In some cases, alternative treatments may be considered to minimize the risk of liver-related complications.
It is important for healthcare providers and patients to work together to assess the benefits and risks of metformin use in the context of liver disease and to make informed treatment decisions based on individual health needs.
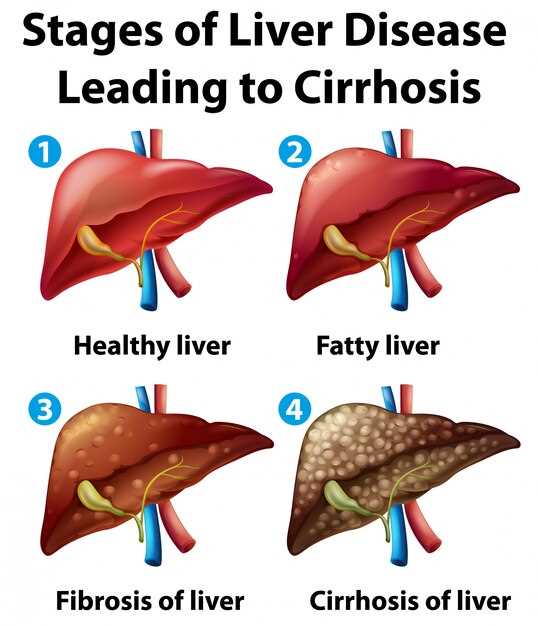
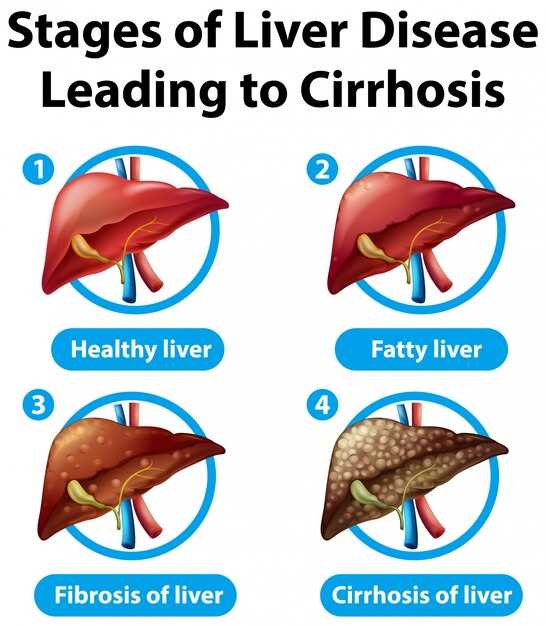
End Stage Liver Disease: Symptoms and Treatment
End stage liver disease refers to an advanced stage of liver damage where the liver is no longer able to function properly. This condition can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention. Recognizing the symptoms of end stage liver disease is crucial for timely intervention and treatment.
- Jaundice: A yellowing of the skin and eyes due to the buildup of bilirubin in the bloodstream.
- Ascites: Fluid retention in the abdomen leading to swelling and discomfort.
- Portal Hypertension: Increased pressure in the portal vein causing complications like varices and splenomegaly.
- Hepatic Encephalopathy: Cognitive impairment and confusion due to the liver’s inability to detoxify ammonia.
- Easy Bruising and Bleeding: Impaired blood clotting due to decreased production of clotting factors by the liver.
Treatment for end stage liver disease may include medication, dietary changes, lifestyle modifications, and in severe cases, liver transplantation. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider for proper management and care. Early detection and intervention can help improve outcomes for individuals with end stage liver disease.
Recognizing Symptoms of End Stage Liver Disease
End-stage liver disease is a serious condition that can have severe and debilitating symptoms. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for early detection and treatment. Some common symptoms of end-stage liver disease include:
| Ascites: Accumulation of fluid in the abdomen causing swelling |
| Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes due to a buildup of bilirubin |
| Easy bruising and bleeding: Due to decreased production of clotting factors |
| Fatigue: Extreme tiredness and weakness |
| Mental confusion: Difficulty concentrating, memory problems |
| Spider-like blood vessels: Small, spider-like blood vessels on the skin |
It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms, as end-stage liver disease requires prompt treatment to prevent further complications.
Treatment and Management Options for Liver Disease
When dealing with end stage liver disease, proper treatment and management are essential to improve the patient’s quality of life and potentially slow disease progression. In the case of liver disease related to metformin use, a comprehensive approach is required to address both the underlying condition and the potential impact of the medication.
Medical Interventions
Medical interventions for end stage liver disease may include medications to manage symptoms, control complications, and improve liver function. Patients with liver disease caused by metformin may require adjustments to their medication regimen to minimize further liver damage.
Lifestyle Changes
Patients with end stage liver disease should adopt healthy lifestyle habits to support liver function and overall well-being. This may include maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, avoiding alcohol and harmful substances, and managing comorbid conditions such as obesity and diabetes.
Ultimately, a collaborative approach involving healthcare providers, patients, and caregivers is crucial in the treatment and management of liver disease. By addressing the potential impact of metformin on liver function and implementing appropriate interventions, individuals with end stage liver disease can enhance their quality of life and potentially improve their long-term prognosis.
Impact of Metformin on End Stage Liver Disease
Metformin, a commonly prescribed medication for type 2 diabetes, has been a subject of interest in the management of end-stage liver disease. Research suggests that Metformin may offer potential benefits for individuals with liver disease, as it has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation, and promote weight loss.
Studies have indicated that Metformin may play a role in the prevention of liver-related complications and may help to slow the progression of liver disease. By improving insulin sensitivity, Metformin can potentially reduce the risk of developing complications such as fatty liver disease and cirrhosis.
Additionally, Metformin has been shown to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in the liver. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals with liver disease, as inflammation and oxidative stress are key factors in the development and progression of liver damage.
Overall, the impact of Metformin on end-stage liver disease is promising, and further research is needed to fully understand its potential benefits in this population. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine if Metformin is a suitable treatment option for you if you have liver disease.
Benefits of Metformin in Liver Disease Management
Metformin, a commonly prescribed medication for diabetes, has shown potential benefits in the management of liver disease. Here are some key advantages:
1. Improved Insulin Sensitivity
Metformin helps improve insulin sensitivity in the body, which is beneficial for patients with liver disease. By enhancing insulin action, Metformin can help regulate blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications associated with liver disease.
2. Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Studies have suggested that Metformin may possess anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce inflammation in the liver. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals with liver disease, as inflammation plays a key role in disease progression.
Overall, the benefits of Metformin in liver disease management are promising, but it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting or changing any medication regimen.
Potential Risks and Considerations with Metformin Use
Metformin is generally considered a safe and effective medication for managing diabetes. However, like any medication, it comes with potential risks and considerations that should be taken into account.
1. Gastrointestinal Issues
One of the most common side effects of metformin is gastrointestinal upset, including diarrhea, abdominal pain, and nausea. These symptoms typically improve over time as the body adjusts to the medication, but they can be bothersome for some individuals.
2. Lactic Acidosis Risk
While rare, metformin has been associated with a serious condition called lactic acidosis, which is a buildup of lactic acid in the blood. This condition can be life-threatening and is more likely to occur in individuals with kidney or liver problems.
It’s essential to monitor kidney function regularly while taking metformin to reduce the risk of lactic acidosis.
It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before starting metformin to discuss any potential risks, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications.
It’s important to weigh the benefits of metformin in managing diabetes against the potential risks to make an informed decision about its use.
