
Are you concerned about your white blood cell count while taking Metformin?
Metformin is a commonly prescribed medication for managing diabetes, but some individuals may experience changes in their white blood cell levels while on this drug.
It is important to monitor your white blood cell count regularly with your healthcare provider to ensure that Metformin is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about the potential effects of Metformin on white blood cell count and how to manage this side effect with expert guidance.
Understanding Metformin
Metformin is a commonly prescribed medication for managing type 2 diabetes. It belongs to a class of drugs called biguanides, which work by lowering blood sugar levels in the body. Metformin helps the body respond better to insulin and reduces the amount of glucose produced by the liver.
Metformin is typically taken orally in the form of tablets or extended-release tablets. It is important to follow the dosage instructions provided by your healthcare provider to ensure its effectiveness in controlling blood sugar levels.
Metformin is often prescribed alongside lifestyle changes such as regular exercise and a healthy diet to effectively manage diabetes and improve overall health.
Key benefits of Metformin
Metformin is a commonly prescribed medication for managing type 2 diabetes. It offers several key benefits, including:
- Effectively lowers blood sugar levels
- Improves insulin sensitivity
- Reduces the amount of glucose produced by the liver
- Helps with weight management
- May lower the risk of heart disease in diabetes patients
Understanding these benefits can help individuals with diabetes make informed decisions about their treatment options. Consult your healthcare provider to learn more about how Metformin can benefit your health.
How Metformin affects white blood cell count
Metformin is a widely used medication for the management of diabetes. While Metformin is generally well-tolerated by most individuals, it can sometimes lead to a decrease in white blood cell count, a condition known as leukopenia.
White blood cells are essential for the body’s immune system, as they help fight off infections and diseases. When the white blood cell count drops, it can put individuals at a higher risk for infections.
Factors influencing white blood cell count with Metformin:
- Dose: Higher doses of Metformin may increase the likelihood of developing leukopenia.
- Duration of use: Long-term use of Metformin can sometimes lead to a decrease in white blood cell count.
If you experience any symptoms of low white blood cell count, such as persistent infections or fatigue, it is important to consult your healthcare provider immediately. They can monitor your blood cell count and adjust your medication if necessary to ensure your safety and well-being.
Managing Low White Blood Cell Count
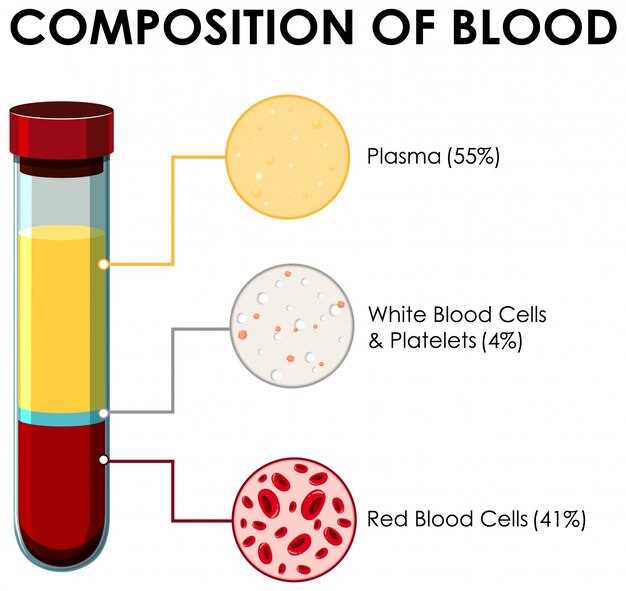
Managing a low white blood cell count, also known as leukopenia, is essential for maintaining your overall health and immune function. Here are some tips to help you boost your white blood cell count naturally:
- Eat a balanced diet: Consuming a variety of nutrient-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help support your body’s ability to produce white blood cells.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help flush out toxins and support the proper functioning of your immune system.
- Get enough sleep: Adequate rest is crucial for immune function and overall health. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night.
- Manage stress: Chronic stress can weaken the immune system. Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga to reduce stress levels.
- Exercise regularly: Engaging in moderate physical activity can help boost your immune system and promote the production of white blood cells. Aim for at least 30 minutes of exercise most days of the week.
Remember, it’s important to consult with your healthcare provider before making any significant changes to your diet or lifestyle, especially if you are managing a medical condition like leukopenia.
Tips for boosting white blood cell count
Boosting your white blood cell count can help improve your overall immune system and health. Here are some tips to help increase your white blood cell count:
| 1. Eat a balanced diet: | Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats in your diet to provide essential nutrients for white blood cell production. |
| 2. Stay hydrated: | Drink plenty of water throughout the day to keep your body hydrated, which supports the production of white blood cells. |
| 3. Get regular exercise: | Engage in moderate physical activity regularly to boost circulation and promote the production of white blood cells. |
| 4. Get enough sleep: | Ensure you get adequate rest each night as sleep is crucial for the body’s immune function and white blood cell production. |
| 5. Manage stress: | Practice stress-reducing activities such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises to support a healthy immune system and white blood cell count. |
Consulting your healthcare provider
It is essential to consult your healthcare provider before making any changes to your medication or treatment plan. Your healthcare provider will be able to provide personalized advice based on your individual health needs and medical history. They can also help you understand the potential risks and benefits of using Metformin and its impact on your white blood cell count.
By discussing your concerns with your healthcare provider, you can work together to find the best approach to managing your condition and maintaining optimal white blood cell levels. Your healthcare provider can also monitor your white blood cell count through regular blood tests and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
Remember, your healthcare provider is there to support you in your health journey and help you make informed decisions about your treatment options. By seeking their guidance and expertise, you can ensure that you are taking the appropriate steps to safeguard your health and well-being.
